Surface predictor of overturning circulation and heat content change in the subpolar North Atlantic
Abstract
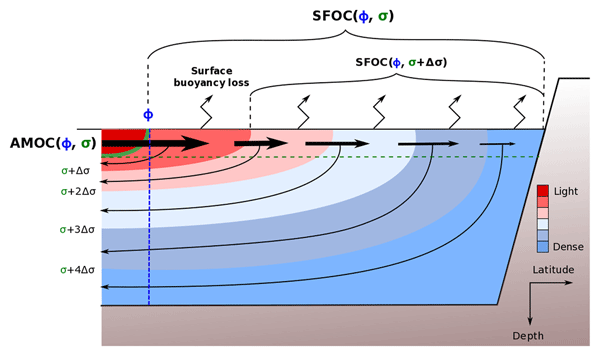
The Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) impacts ocean and atmosphere temperatures on a wide range of temporal and spatial scales. Here we use observational datasets to validate model-based inferences on the usefulness of thermodynamics theory in reconstructing AMOC variability at low frequency, and further build on this reconstruction to provide prediction of the near-future (2019–2022) North Atlantic state. An easily observed surface quantity – the rate of warm to cold transformation of water masses at high latitudes – is found to lead the observed AMOC at 45∘ N by 5–6 years and to drive its 1993–2010 decline and its ongoing recovery, with suggestive prediction of extreme intensities for the early 2020s. We further demonstrate that AMOC variability drove a bi-decadal warming-to-cooling reversal in the subpolar North Atlantic before triggering a recent return to warming conditions that should prevail at least until 2021. Overall, this mechanistic approach of AMOC variability and its impact on ocean temperature brings new key aspects for understanding and predicting climatic conditions in the North Atlantic and beyond.