Preparing the New Phase of Argo: Scientific Achievements of the NAOS Project
Abstract
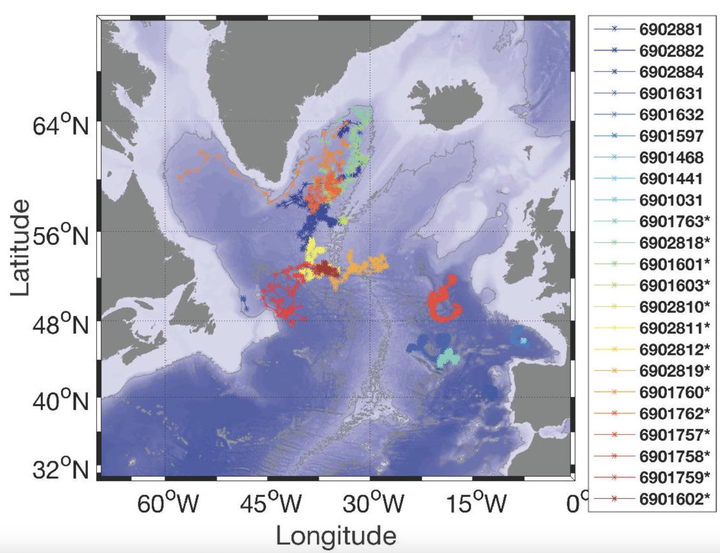
Argo, the international array of profiling floats, is a major component of the global ocean and climate observing system. In 2010, the NAOS (Novel Argo Observing System) project was selected as part of the French “Investissements d’Avenir” Equipex program. The objectives of NAOS were to consolidate the French contribution to Argo’s core mission (global temperature and salinity measurements down to 2000 m), and also to develop the future generation of French Argo profiling floats and prepare the next phase of the Argo program with an extension to the deep ocean (Deep Argo), biogeochemistry (BGC-Argo) and polar seas. This paper summarizes how NAOS has met its objectives. The project significantly boosted France’s contribution to Argo’s core mission by deploying more than 100 NAOS standard Argo profiling floats. In addition, NAOS deployed new-generation floats as part of three scientific experiments: biogeochemical floats in the Mediterranean Sea, biogeochemical floats in the Arctic Ocean, and deep floats with oxygen sensors in the North Atlantic. The experiment in the Mediterranean Sea, launched in 2012, implemented and maintained a network of BGC-Argo floats at basin scale for the first time. The 32 BGC-Argo floats deployed and about 4000 BGC profiles collected have vastly improved characterization of the biogeochemical and ecosystem dynamics of the Mediterranean. Meanwhile, experiments in the Arctic and in the North Atlantic, starting in 2015 and deploying 20 Arctic BGC floats and 23 deep floats, have provided unique observations on biogeochemical cycles in the Arctic and deep-water masses, as well as ocean circulation variability in the North Atlantic. NAOS has therefore paved the way to the new operational phase of the Argo program in France that includes BGC and Deep Argo extensions. The objectives and characteristics of this new phase of Argo-France are discussed in the conclusion.